It’s no secret, organizations around the globe are moving their workloads to public cloud platforms such as Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google cloud. These platforms offer tremendous benefits including ease of management, reduced costs, increased security, and technological advancements. No doubt, the benefits offered by the public cloud outweigh those offered by IT infrastructure running in a traditional on-premise environment. However, not properly controlling these workloads can lead to an exponential rise in monthly cloud bills. Here are some proven tactics, divided by prevention and cure (corrective) techniques to help control monthly expenditures on public clouds. These are especially important for oil and gas companies where they are increasingly using cloud computing for field applications and services, and cost savings are often ignored.
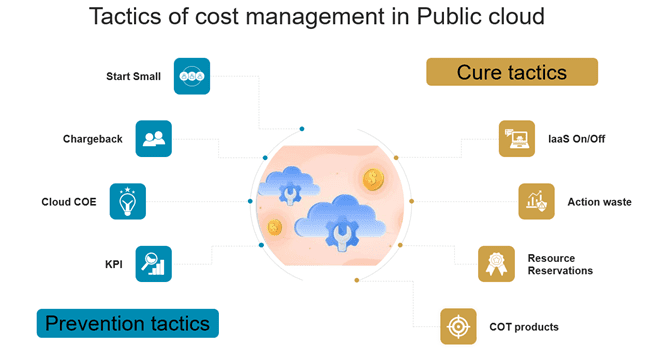
Prevention
To avoid large unnecessary investments initially and control monthly spending, it’s critical to carefully plan upfront. Here are some tactics that will lead to reducing costs:
- Start small
Traditional data center environments required large investments to account for future growth and evolving business strategies. However, strategies evolve over time and data center infrastructures quickly become outdated. Conversely, public cloud solutions are agile and can address ever-evolving business strategies. So start small and add infrastructure as needed; this will result in substantial savings.
- Chargeback
Many organizations centralize their IT budget with minimal or no charge back policies for business applications used outside of IT by different business units that are using the cloud to run their services. Because these groups don’t have “skin in the game”, they really do not fully realize the expenses they may be causing. Having a chargeback to business units leads to better management of cloud resources and cutting down waste. Business units can implement better cost optimization techniques such as full resource utilization, using free cloud credits and spot instances for fault-tolerant workloads, and rightsizing instances.
- Cloud COE
Implement a centralized IT team COE (cloud center of excellence) who are experts in this field. These specialized application or project teams can provide necessary guidance, architecture, and cost optimization training that will lead to lower costs and a better system overall.
- KPIs
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluate these goals and met targets at least once a year. Incorporate cost and performance optimization KPIs into team members’ appraisal goals. Research has shown this tactic brings in innovative ideas from the employees themselves including recommending a cloud hosting solution that is best-in-class with reduced monthly costs.
Cure
Focus on cost optimization in your day-to-day IT operations by using cure (corrective) tactics as described below:
- IaaS ON/OFF
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is the most used service in the public cloud. Cloud providers charge by the number of hours a service is running on their platform each month. Therefore, it is highly recommended that any virtual machine (VM) not required to run during non-production times (i.e., during the weekend) is shut down. This simple step can result in more than 25% of savings per VM. Most cloud platforms provide ample opportunities to do this as a self-service to end users, even with their mobile phones. Shutdowns can also be auto scheduled for Power ON and Off using Artificial Intelligent (AI) software e.g., (ParkMyCloud), which provides the historical trend of VM usage and suggests intelligent ON and OFF schedules, as well as ways to automate the entire process. Making these types of small investments can bring significant cost optimization.
- Identify waste and take prompt action
In typical day-to-day IT operations cloud resources are often wasted because of flaws in the IT processes. If they are not addressed and removed in a timely manner, they can incur significant costs. Cloud providers offer native advisors and CLI (command line interface) utilities that watch for stale resources and delete them quickly, resulting in significant savings. Top waste resources include unattached disks and stale virtual machines.
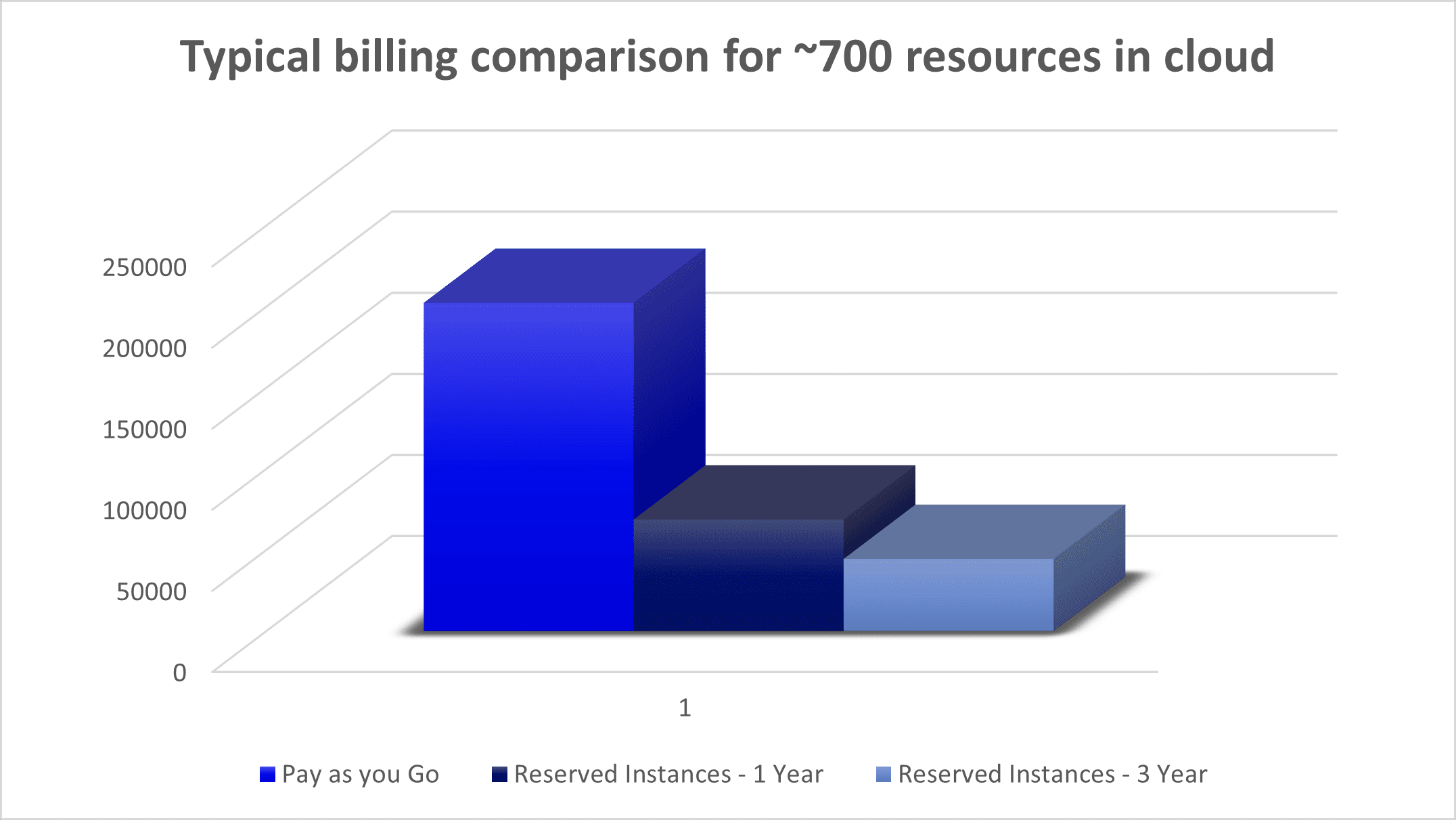
- Resource reservations
Cloud charging options are either “pay as you go” or on a commitment term bases, typically 1-year or 3-years called reserving resources. Because reservations are much more cost efficient, it is recommended to determine the minimum number of workloads that are required for the long run and reserve them upfront. And if business directions change, there will always be other potential candidates that can accommodate that reservation.
 COTS products
COTS products
Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) software, such as IBM Turbonomic, can help better day-to-day management of your cloud resources. Because charges in the cloud are primarily based on the number of CPUs and memory reserved by the resource, these tools provide smart recommendations that boost resource performance and save money. These types of small investments empower IT operation teams as they can make decisions based on factual historical data. The COTS’s intelligent capabilities can help teams tweak an environment based on unique business and IT scenarios. It can also help achieve significant cumulative net savings. For example, over three years, more than 1,000 recommendations were executed on 1500 cloud VMs each week, resulting in cumulative savings of ~$600K.
Conclusion
Cloud costs are a substantial expenditure in modern IT. If it goes uncontrolled, it can incur significant losses and increase monthly IT budgets for the organizations. To combat this, there are tactics required on two fronts. One is “prevention” where cost management is governed by business policies and their enforcement. The other is “cure” which focuses on empowering IT operations to take corrective measures and cut waste to save cash for the company. In this current era where oil field companies are trying to cut cost in operations, these cloud saving tactics brings some relief and help optimize spending.
Born in Delhi, India, Sumit was recently relocated to Houston, TX and promoted to Solution Architect for a world leader in the oilfield services industry. Before moving to the U.S., Sumit spent most of his life in several cities throughout India and UK including Pune, Gurugram, Bangalore and London.
Oil and gas operations are commonly found in remote locations far from company headquarters. Now, it's possible to monitor pump operations, collate and analyze seismic data, and track employees around the world from almost anywhere. Whether employees are in the office or in the field, the internet and related applications enable a greater multidirectional flow of information – and control – than ever before.