More than 4.6 trillion cubic feet of natural gas were flared globally in 2019. The potential value of this flared gas could be as high as US$24bn, if priced at the European gas benchmark, says leading data and analytics company GlobalData.
Soorya Tejomoortula, Oil and Gas Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “Key countries in the world flared more than 3.5 trillion cubic feet of natural gas in 2019, which constituted more than US$9.5bn in foregone revenue – when priced at U.S. Henry Hub gas prices – and over US$19bn when priced at UK NPB prices.”
The company’s report, ‘Gas Flaring Market Analysis 2020’, found that some of the major oil producing countries in the world such as Iraq, Iran, Russia, the U.S., Venezuela, Nigeria, Libya, Indonesia, Angola and Algeria were jointly responsible for over 80% of the associated gases flared globally in 2019. Recently, flaring in countries such as the US and Iraq has increased considerably due to a corresponding growth in crude oil production.
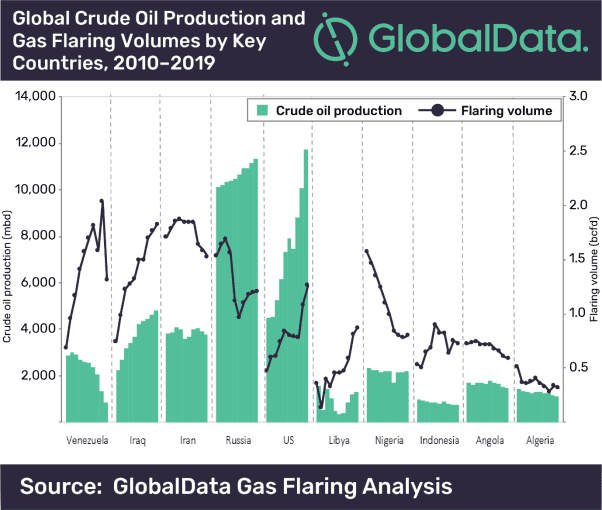 However, some of the major oil producing countries such as Nigeria have been able to decrease associated gas flaring in the past decade due to enforcement of government regulations, re-injection of associated gas and increasing utilization of associated gas.
However, some of the major oil producing countries such as Nigeria have been able to decrease associated gas flaring in the past decade due to enforcement of government regulations, re-injection of associated gas and increasing utilization of associated gas.
Russia is also able to reduce flaring marginally despite growing crude oil production due to toughening regulatory measures. Also, companies such as SIBUR are actively using associated gas as a feedstock for their petrochemical operations, contributing an overall decline in flaring volumes.
Tejomoortula concludes: “Utilization of associated gas is one of the most effective means to reduce gas flaring and benefits both the upstream producers and the environment.
“Opportunities for use of associated gas include re-injection of gas into wells to enhance recovery of oil, using as a feedstock for petrochemical plants, and for power generation. Small-scale solutions for utilization include mini GTL (gas to liquids) plants, mini/small-scale liquefaction plants, and compressed natural gas (CNG) plants.”
Oil and gas operations are commonly found in remote locations far from company headquarters. Now, it's possible to monitor pump operations, collate and analyze seismic data, and track employees around the world from almost anywhere. Whether employees are in the office or in the field, the internet and related applications enable a greater multidirectional flow of information – and control – than ever before.