Assets integrity is essential to maintain safety, regulatory compliance and productivity. Balancing this imperative against potential cost is a constant challenge. These days, the oil and gas industry is facing increased pressure to reduce risks and improve safety and reliability with cost effectiveness.
The management of failure analysis has a strategic importance within the oil and gas industry from an economical, planning, engineering and organizational point of view. The analysis of the failure data allows for a methodical and as far as possible approach for the management of failure, and can make considerable improvements in the establishment of work and in the decision-making processes.
A panel of experts, made up of quality professionals, discipline engineers, HSE specialists and operators, is formed to assign a risk based inspection level. Taking into consideration design complexity factors, manufacturing complexity factor, installation complexity factors and probability of near accidents, occupational and environmental accidents. Five probability classes and five severity categories, which consider three impact categories (health and safety, environmental and reputation), have been defined.
Risk based inspection (RBI) is the process of developing a prioritized inspection plan based on knowledge of the risk of failure of equipment. It involves quantitative assessment of the probability of failure (PoF) and the consequence of failure (CoF) associated with each equipment/material.
RBI balances inspection costs and risk by using appropriate technology, inspection and maintenance planning. RBI is an approach for asset integrity management which seeks to optimize inspection activities based on the likelihood and consequence of failure of components and systems. Using this methodology, inspection frequency is highest for the highest risk systems, and the interval between inspections is lengthened for those systems that have the lowest risk. This approach to inspection can significantly reduce maintenance costs and unplanned downtime.
RBI is an approach to asset integrity management which seeks to optimize inspection activities based on the likelihood and consequence of failure of components and systems. It is to develop the best approach for inspection activities using risk assessment and risk rating.
Objectives
The primary objectives of implementing of a risk based inspection program is to produce an inspection strategy that clearly states:
What needs to be inspected? Identify equipment and material that need to be inspected.
When will it be inspected? Specify the inspection interval.
How will it be inspected? Identify the technique that needs to be applied.
Risk Based Inspection
Implementing a risk based inspection program can provide benefits including reduced risk, optimized inspection planning, and cost savings. The output of an RBI assessment is an inspection plan that identifies the inspection methods, extents, and intervals necessary to mitigate the identified risks.
At its most basic level, RBI involves looking at the likelihood of a piece of equipment failing versus the consequences of the failure of the equipment and ultimately assigning a value representing the risk associated with that piece of equipment.
When all the identified equipment has been assigned a risk value, inspections can be prioritized to ensure that they reduce the risk of failure. By identifying and prioritizing equipment by risk, limited inspection and maintenance budgets can be optimized to focus inspection resources and maintenance dollars on the highest risk equipment.
Once inspection and maintenance activities have been completed, risk should be recalculated taking into consideration inspection effectiveness and risk mitigation steps. The inspection plan should also be reviewed to make the best use of limited inspection and maintenance resources.
A typical RBI implementation includes following four steps:
- Data Collection
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Evaluation
- Inspection Planning
Data Collection
To implement RBI strategy, data collection is very important, and sets the foundation for successful risk assessment.
The following data are required for RBI:
- Design and construction data
- Process and operating data
- Inspection and Maintenance History
Risk Assessment
A risk assessment is a process of identifying potential machine/equipment failure. A risk assessment needs to be carried out to identify items which had negligible probability of failure (PoF) or consequence of failure (CoF). Develop a cross-functional team consisting of inspection personnel, discipline engineers, chemical process engineers, metallurgists, corrosion specialists and management members. A risk assessment meeting needs to be organized by an RBI facilitator (inspection personnel) to identify the associated risks.
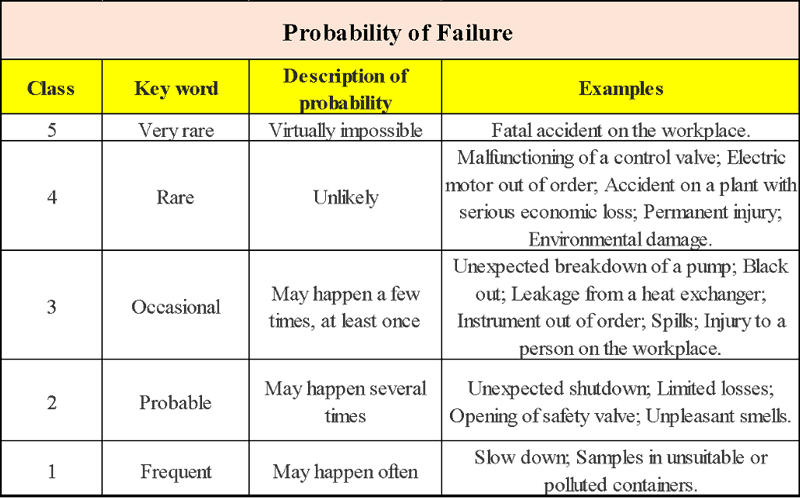
Probability of Failure (PoF)
Determine how likely a loss of containment could occur based on:
- Damage mechanisms and rates
- Effectiveness of inspection program
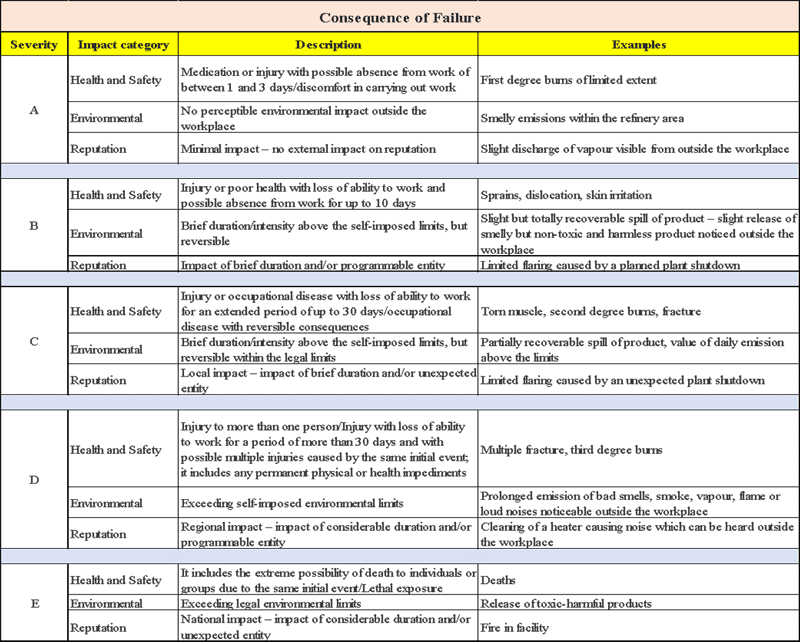
Consequence of Failure (CoF)
Estimate impacts of loss of containment for:
- Safety and health
- Environmental
- Economic
Risk Evaluation
Risk evaluation is the process of comparing the results of risk analysis with risk criteria to determine the inspection level. Risk is the combination of the probability of some event occurring during a time period of interest and the consequences (generally negative) associated with the event. Risk can be calculated by following equation:
Risk = Probability of failure × Consequence of failure
Table 1 shows probability of failure and Table 2 shows consequences of failure:
The figure below shows a typical decision matrix to assign inspection criticality rating.
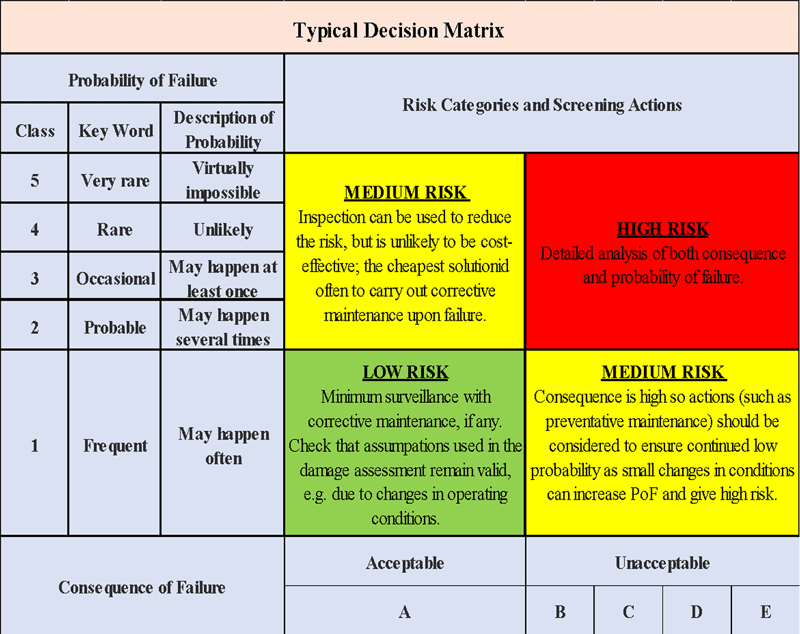
Develop a comprehensive understanding of risks and take factors into account that contribute to risk. It can be done by analyzing the likelihood and consequences of failure. Develop a comprehensive understanding of mitigation measures and rank facilities according to relative risk. This rating will be used to determine the inspection level.
Inspection Planning
An RBI facilitator will develop a cost-effective inspection program considering criticality and inspection level to ensure asset integrity and reliability. Identify and understand risk drivers to prioritize inspection-related activities. This inspection program should include the following points:
- Procedures and practices
- Frequency of inspection
- Tools and techniques
- Coverage
- Recourse
Prioritize and focus inspection resources on those that pose the highest risks in accordance with RBI priorities. Careful selection of the optimum inspection techniques can provide effective means of monitoring the condition of critical pressure systems without the risks and production disruption associated with internal inspections.
Benefits
Decision-making assessment using the risk matrix must be carried out by a special team whose experience must guarantee thorough competency concerning all aspects of the specific operation being examined. The work procedure which was developed has also led to a common and easily comprehensible technical language which is used by all the people who interact in the plants.
RBI is a means of using inspection resources more cost-effectively and with confidence alternative to traditional inspection. It also enables one to make inspection decisions informed by greater information and expertise, thereby saving time and money.
RBI principles offer an established methodology for efficient plant maintenance and develop cost-effective management solutions. They allow graded approach to the inspections, in which the most critical equipment is subjected to a more rigorous inspection programme.
RBI is beneficial to reduce unscheduled shutdowns. It manages risk by reducing uncertainty through inspection, and adheres to codes of compliance resulting in increased safety.
RBI methodology proposed in this paper can be adapted and used in many situations which may arise in the oil and gas industry. Using this methodology, it is possible not only to make a failure analysis, but also to estimate the environmental aspects connected with operational activities, the safety risk, and to make an investment analysis.
Disclaimer: This paper does not represent any PSG position and it is in no way related to Prima Strategic Group.
Gaurav Goswami is working with Prima SG Inc. as a project quality manager. He holds Bachelor of Engineering in Mechanical Engineering and Master of Engineering in Mechanical Engineering. Goswami is a member of the American Society for Mechanical Engineers (ASME), and has published many papers in Journals and Magazines. He is ISO 9001 Lead Auditor and has more than 17 years of experience in the oil and gas industry.
Oil and gas operations are commonly found in remote locations far from company headquarters. Now, it's possible to monitor pump operations, collate and analyze seismic data, and track employees around the world from almost anywhere. Whether employees are in the office or in the field, the internet and related applications enable a greater multidirectional flow of information – and control – than ever before.